Mains Power
Mains power (sometimes mains or line) refers to the AC power at the final stage of the electrical grid that is run into most buildings and is available at wall outlets. The voltage used varies throughout the world however in North America the standard is 110 - 127 V AC while Europe is 220 - 240 V AC. There is significant danger in coming into contact with mains as the only limit to the current is a breaker or fuse in the service box for the building which is designed to prevent damage to the building's wiring, not prevent damage to connected devices or electrocution. As such devices with exposed mains power have inherent hazards when they are powered.
Live or Hot Chassis
Some devices such as CRT displays or televisions or radios may have been designed with a live chassis that is connected to mains power. This means touching the chassis while having contact with either neutral or earth ground can complete a circuit and result in a significant electrical shock. These also pose a hazard for diagnostics and can lead to other difficulties such as finding a suitable DC ground reference for taking measurements.
TODO - Document methods of determining a live chassis in an unpowered state.
Filter Caps

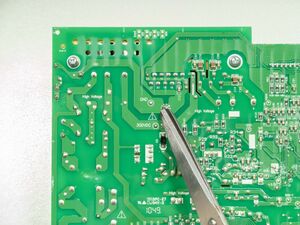
In older DC power supplies it is common to add bulk capacitance to the rectified input voltage from the AC source. These capacitors may be charged up to the level of the AC mains voltage and depending on the design of the power supply may hold that charge after the device has been turned off. If working on a power supply it may be advisable to use a bleeder resistor connection to discharge these capacitors in a controlled manner to avoid the shock hazard.
Voltages Present on Mains Bulk Capacitors
TODO
- V AC often means Vrms AC, 230 Vrms AC will be 325 Vp AC
- Devices with active PFC will have boosted voltages sometimes up to 400 V DC
Safety Capacitors
TODO
- Those are called safety capacitors because their failure can result in parts the user can touch becoming live at mains voltage.
- Things like X and Y class safety capacitors must be replaced with proper safety capacitors of equivalent type, not just any random film or ceramic capacitor.
Earth Leakage Safety Devices
TODO